imate.InterpolateLogdet.bound#
- InterpolateLogdet.bound(t)#
Bound of the interpolation function.
If \(p < 1\), this function is a lower bound, and if \(p > 1\), this function is an upper bound of the interpolation function.
- Parameters:
- tfloat or numpy.array
An inquiry point or an array of inquiry points.
- Returns:
- boundfloat or numpy.array
Bound function evaluated at t. If t is an array, the output is also an array of the size of t.
Notes
Define
\[\tau_{p}(t) = \frac{\Vert \mathbf{A} + t \mathbf{B} \Vert_p}{\Vert \mathbf{B} \Vert_p}\]and \(\tau_{p,0} = \tau_{p}(0)\). A sharp bound of the function \(\tau_{p}\) is (see [1], Section 3):
\[\tau_{p}(t) \leq \tau_{p, 0} + t, \quad p \geq 1, \quad t \in [0, \infty),\]\[\tau_{p}(t) \geq \tau_{p, 0} + t, \quad p < 1, \quad t \in [0, \infty),\]\[\tau_{p}(t) \geq \tau_{p, 0} + t, \quad p \geq 1, \quad t \in (t_{\inf}, o],\]\[\tau_{p}(t) \leq \tau_{p, 0} + t, \quad p < 1, \quad t \in (t_{\inf}, o],\]References
[1]Ameli, S., and Shadden. S. C. (2022). Interpolating Log-Determinant and Trace of the Powers of Matrix \(\mathbf{A} + t \mathbf{B}\). Statistics and Computing 32, 108. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11222-022-10173-4.
Examples
Create an interpolator object \(f\) using four interpolant points \(t_i\):
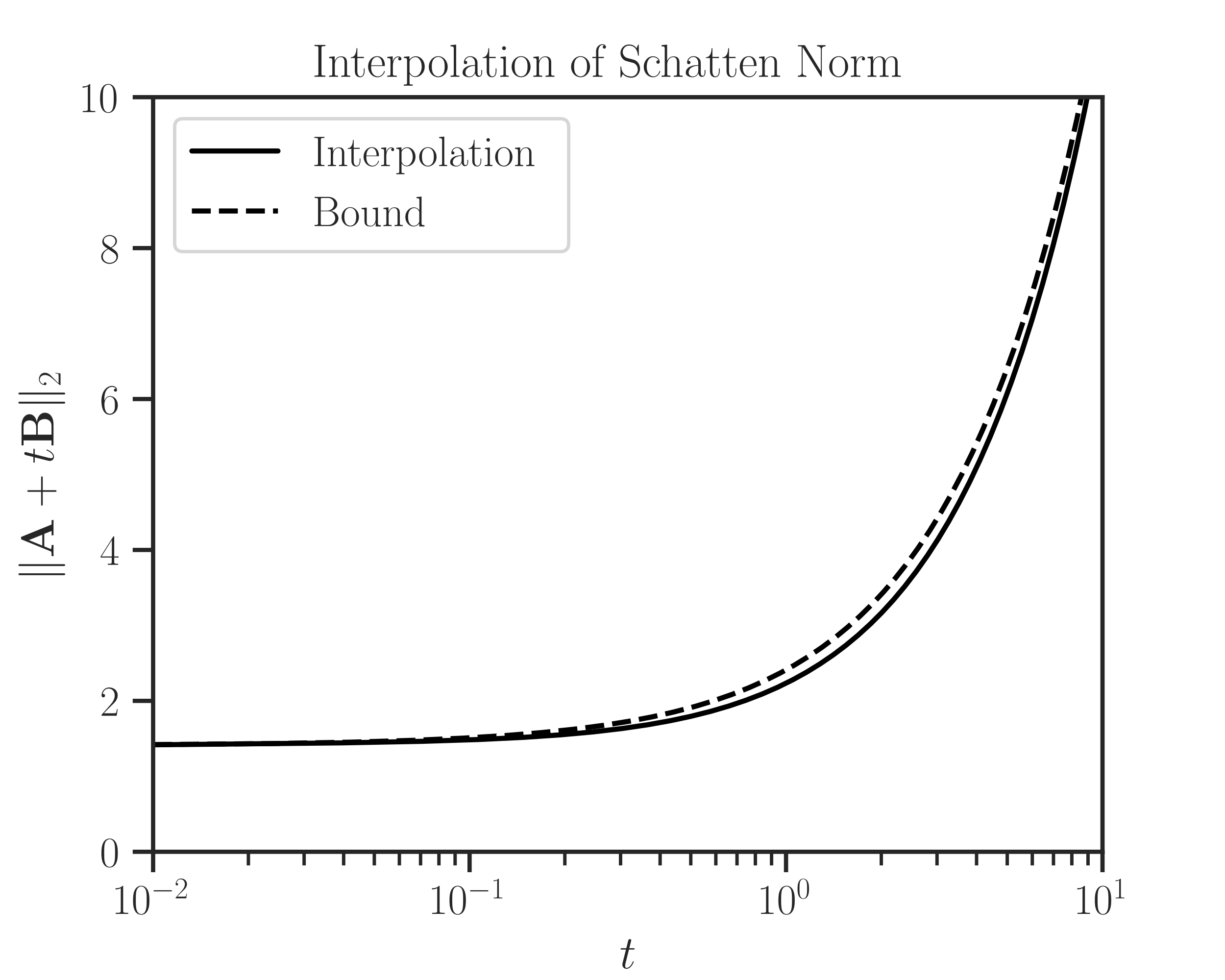
>>> # Generate sample matrices (symmetric positive-definite) >>> from imate.sample_matrices import correlation_matrix >>> A = correlation_matrix(size=20, scale=1e-1) >>> B = correlation_matrix(size=20, scale=2e-2) >>> # Initialize interpolator object >>> from imate import InterpolateSchatten >>> ti = [1e-2, 1e-1, 1, 1e1] >>> f = InterpolateSchatten(A, B, p=2, ti=ti)
Create an array t and evaluate upper bound on t. Also, interpolate the function \(f\) on the array t.
>>> # Interpolate at an array of points >>> import numpy >>> t = numpy.logspace(-2, 1, 1000) >>> bound = f.bound(t) >>> interp = f.interpolate(t)
Plot the results:
>>> import matplotlib.pyplot as plt >>> # Plot settings (optional) >>> from imate._utilities import set_custom_theme >>> set_custom_theme(font_scale=1.15) >>> plt.semilogx(t, interp, color='black', label='Interpolation') >>> plt.semilogx(t, bound, '--', color='black', ... label='Bound') >>> plt.xlim([t[0], t[-1]]) >>> plt.ylim([0, 10]) >>> plt.xlabel('$t$') >>> plt.ylabel('$\Vert \mathbf{A} + t \mathbf{B} \Vert_{2}$') >>> plt.title('Interpolation of Schatten Norm') >>> plt.legend() >>> plt.show()